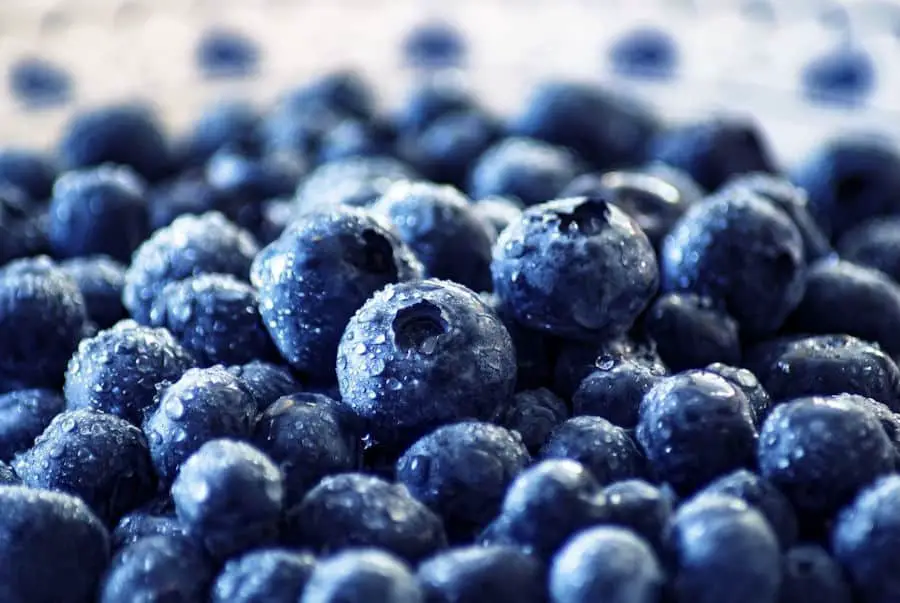
Anthocyanins, the vibrant pigments responsible for the dark purplish-blue, red, and black hues in bilberries, blueberries, Maqui berries, and black currants, serve as potent antioxidants. These berry extracts and powders are essential components in nearly every eye vitamin formula, renowned for their robust antioxidant properties.
In addition to bilberries, blueberries, Maqui berries, and black currants, traces of these same substances can be found in raspberries, strawberries, gooseberries, and cranberries, albeit in much smaller quantities. Anthocyanins also occur in various fruits and vegetables such as sour cherries, plums, purple cabbage, grapes (including red wine), apples, red onions, and sweet potatoes.
The deep blue-purple-black pigment of anthocyanins is not confined to the berries alone; it’s also present in the stems and leaves of the plants. This pigment serves a crucial role, absorbing high-energy blue radiation from sunlight to shield plant cells from photodamage and reduce oxidative stress. By consuming these anthocyanin-rich berries, we aim to safeguard our cells against harmful oxidative stress.
Anthocyanins belong to the Flavonoid class of antioxidants, which are organic and water-soluble. While there are hundreds of anthocyanins, six are commonly found in foods: cyanidin, delphinidin, malvidin, peonidin, pelargonidin, and petunidin. This information is valuable, as you may encounter specific anthocyanins listed in the ‘supplement facts.’
Upon ingestion, anthocyanins are swiftly absorbed by the digestive system but are also rapidly eliminated by the kidneys. They are absorbed within minutes of ingestion and typically clear the body within four hours. (Ref: Anthocyanins: structural characteristics …)
…)
The Multi-Faceted Benefits of Anthocyanins
Antioxidants play a vital role in neutralizing harmful free radicals within our bodies, thus halting or reversing cell damage that may precipitate disease.
Beyond their antioxidant properties, anthocyanins boast a spectrum of bioactive functions, including:
- Anti-inflammatory action
- DNA stabilization
- Anti-cancer potential
- Enhancement of insulin secretion and sensitivity
- Antibacterial properties
Enhancing Eye Health: The Impact of Anthocyanins
Anthocyanins play an important role in promoting eye health through various mechanisms:
- Optimizing Photoreceptor Function: Anthocyanins stimulate the regeneration of rhodopsin, the light-sensing pigment in photoreceptors, thereby facilitating dark adaptation—a vital process for vision in low-light conditions.
- Enhancing Retinal Circulation: Anthocyanins contribute to improved blood circulation in the retina, which is essential for maintaining optimal retinal health, particularly in conditions like low tension glaucoma and macular health.
- Combatting Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: With their potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, anthocyanins help mitigate damage caused by inflammation and oxidative stress in the eye.
While studies have not demonstrated a direct concentration of anthocyanins in the eye, their protective effect on the collagen structure of blood vessels supporting ocular circulation underscores their significance for eye health. While research linking anthocyanins specifically to vision health is limited, existing studies highlight their broader cardiovascular benefits and potential in managing conditions like diabetes. (Ref; Distribution and excretion of bilberry anthocyanins )
)
Macular degeneration
Its anti-oxidant function is beneficial for those with macular degeneration. Anthocyanins have been shown to protect DNA against oxidative stress induced by UV irradiation, which is a source of oxidative stress to the structures of the eye.
Glaucoma
Anthocyanins have been shown to increase vascular blood flow. This is significant for those with low tension glaucoma (Normal Tension Glaucoma, NTG). Studies have shown that increased blood flow in these NTG patients benefited with an improvement in visual field and visual acuity.
If you are interested in glaucoma herbal treatments see article:
5 Novel Natural Dietary Supplements for Treatment and Control of Glaucoma
Diabetic Retinopathy
Studies of diabetic patients (and mice) given anthocyanins experienced a beneficial effect on lowing fasting plasma glucose levels and preventing insulin resistance.
The Potency of Bilberry
Bilberry, renowned for its unparalleled concentration of anthocyanins, stands out as a powerhouse of antioxidant capability.
Native to Europe, bilberry thrives as a small, purplish-blue fruit akin to its American counterpart, the blueberry, yet more closely related to huckleberries. Its vibrant hue signifies the presence of anthocyanins, the active ingredient responsible for its antioxidant prowess.
Traditionally, bilberry has been utilized in herbal medicine to address an array of ailments, including stomach issues, diarrhea, scurvy, infections, and kidney stones. When combined with nutrients like vitamins C, E, and A, it is believed to bolster blood vessel integrity by reducing vascular permeability and capillary fragility.
Bilberry and the Eye
Bilberry’s association with vision health dates back to World War II, with Royal Air Force pilots attributing improved night vision to bilberry consumption. However, this notion, debunked as a myth, lacks empirical evidence.
The only study that I found that comes close to improving vision in healthy subjects was a 2005 study which concluded that given 100 mg/day purified extract of anthocyanin for 4 weeks, improved eyestrain and contrast sensitivity in nearsighted subjects. (Ref: Purified high-dose anthocyanoside oligomer …)
…)
Bilberry and Myopia Control. A German clinical trial using Difrarel®E (Bilberry extracts anthocyanosides and vitamin E) with 36 patients who had progressive myopia, were treated for 14½ months. Twenty nine patients saw a stabilization of any myopic changes and stable or improved visual acuity.
Bilberry and cataracts. There is a study that linked bilberry extract with vitamin E (using Difrarel®E) as a way of halting the progression of cataracts.
Bilberry and Glaucoma. Another study done on patients with normal tension glaucoma showed an improvement in visual function with a combination of Gingko biloba and bilberry extract . (Open angle glaucoma is the more common form of glaucoma.) At this time there is no herbal substitution recommendations for the treatment of glaucoma.
. (Open angle glaucoma is the more common form of glaucoma.) At this time there is no herbal substitution recommendations for the treatment of glaucoma.
Bilberry and Diabetic Eye Disease. Bilberry has also been recommended for diabetics as a way of glucose control and stabilizing blood vessels to prevent bleeding. This suggests that it may play a role in stabilizing the retinopathy associated with diabetic eye disease.
Bilberry Supplements and Dosages
Bilberry has the highest concentration of the active substance, anthocyanin. Bilberry supplement preparations are in the form of extracts, preservatives, powders, and liquids.
When considering bilberry supplements, it’s imperative to ascertain the percentage of anthocyanin content, with 25% being the minimum recommended concentration. Dosages typically range from 20 to 60 mg per capsule, with a suggested intake of 2 to 3 capsules daily, totaling 200 mg.
Safety and Side Effects of Bilberry Extract
Bilberry has been determined to be safe when consumed appropriately. It has no reported contraindications. Although relatively safe, it is recommended that high doses for extended periods of time could be toxic.
The Power of Blueberries
Blueberries have earned the esteemed title of ‘superfood’ due to their remarkable antioxidant activity, with anthocyanins constituting 60% of their antioxidants. Renowned for their myriad health benefits, blueberries are recommended for combating cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases, and supporting vision health.
Research highlights the diverse therapeutic potential of blueberry constituents:
- Anti-cancer Properties: Blueberries contain active ingredients with anti-cancer properties, offering promise in cancer prevention and treatment.
- Anti-diabetic Benefits: Blueberries exhibit anti-diabetic effects, making them valuable in managing and preventing diabetes-related complications.
- Anti-obesity Effects: Particularly significant for diabetic retinopathy, the anti-obesity properties of blueberries contribute to overall health and may aid in mitigating diabetic complications.
- Neuroprotection against Neurodegenerative Diseases: Blueberries demonstrate neuroprotective effects, particularly beneficial in combating age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and other neurodegenerative disorders.
- Anti-inflammatory Action: Blueberries possess potent anti-inflammatory properties, guarding against light-induced retinal injury and supporting ocular health.
Harnessing the power of blueberries as a dietary staple offers a natural and effective approach to promoting overall health and safeguarding vision.
Enhancing Eye Health with Blueberries
The retina, with its high metabolic rate and constant exposure to UV irradiation, faces considerable oxidative stress. Limited studies have suggested a potential link between blueberry consumption and a decreased risk of age-related macular degeneration.
Supplementing with Blueberries
When considering commercially available blueberry supplements, many typically contain 400 to 500 mg of blueberry extract. However, these labels often do not specify the anthocyanin content or percentage but encompass various other active compounds found in blueberries.
The designation of ‘wild’ blueberries as the extract source implies a higher antioxidant content, attributed to the harsher growing conditions compared to cultivated berries.
Determining the clinically effective dose for the health benefits of blueberry extract remains uncertain. A moderate daily intake of whole blueberries amounts to approximately 1/3 cup, providing an estimated 50 mg of anthocyanins.
The Unique Qualities of Maqui Berries
Maqui berries hail from the southern regions of Chile and Argentina in South America, boasting a striking dark blue-purple hue akin to North American blueberries and European bilberries. Like other berries, maqui berries contain anthocyanins, offering similar health benefits.
However, what sets them apart is their elevated concentration of a specific anthocyanin: delphinidin-glucoside. Surpassing bilberries, blueberries, and black currants, this distinctive feature contributes to the exceptional antioxidant potency of maqui berries.
Maqui Berry’s Potential for Eye Health
Despite limited research, Maqui berry shows promise in addressing ocular health and diseases. Notably, it has been explored as a treatment for dry eye, with a standardized extract known as MaquiBright®.
A 2014 study yielded encouraging results, indicating that administering 60 mg of Maqui berry extract over 60 days led to increased tear fluid volume in patients. This effect is attributed to its anti-inflammatory properties targeting the lacrimal glands, likely due to the higher concentration of the anthocyanin delphinidins, which are known to accumulate in these glands.
(Ref study: MaquiBright™ standardized maqui berry extract  … )
… )
(Ref: manufacturer website: MaquiBright )
)
Supplementing with Maqui Berry
MaquiBright® is a standardized extract produced by a manufacturer and supplied to other manufacturers as a raw ingredient. It is standardized to 25%, which represents delphinidins(a specific type of anthocyanin) and 35% anthocyanins. MaquiBright® can be found in several commercially available vision supplements.
The Benefits of Black Currants for Eye Health
Black currants, small purplish-black berries commonly found across Asia, Europe, and New Zealand, have a rich history in traditional Asian medicine, renowned for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Additionally, they are believed to possess antibacterial and antiviral activity, further adding to their therapeutic potential.
In terms of eye health, black currants share similarities with other anthocyanin-rich berries mentioned previously. The essential active ingredients are not only present in the berries but also in the seeds, commonly found in supplements as black currant seed oil. This oil contains additional beneficial compounds such as Vitamin C and gamma-linolenic acid (GLA), an omega-6 fatty acid.
GLA, known for its anti-inflammatory properties, is not synthesized by the body and must be obtained through diet. Vitamin C, an antioxidant, plays an important role in combating chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which contribute to various eye diseases. Together, these components make black currant seed oil a valuable addition to eye health regimens.
The GLA reduces inflammation and the symptoms of dry eye. Sellers of black currant seed oil advertise it as a supplement for eye fatigue and discomfort. This claim is based on a study indicating less symptomatic eye fatigue experienced by users of technology, which were supplemented with black currant anthocyanin extracts. (Ref: Effects of black current anthocyanoside )
)
Supplementing with Black Currants
Black currant supplements are available in various forms, including juice, fruit powders, extracts, and softgels containing black currant seed oil. However, standardized dosages for black currant supplements are lacking. In clinical studies, extracts typically contain 50 mg of active anthocyanin ingredients.
Softgel supplements containing black currant seed oil are commonly produced, with manufacturers specifying the amount of the active ingredient, gamma-linolenic acid (GLA).
In the End…
Throughout centuries, berries and their extracts have been integral components of traditional medicines. The anthocyanin class of organic compounds, renowned for their potent antioxidant properties, have been extensively studied and shown to exert numerous bioactive effects that benefit human health.
While definitive studies on the relationship between anthocyanins and vision are still emerging, accumulating evidence suggests a potential link between these bioactive substances and a reduced risk of eye disease.
Berry supplements also exhibit effects on blood clotting, exerting anti-platelet aggregation activity. This aspect is particularly significant for individuals taking anticoagulants or preparing for surgery. As always, it is important to consult with your physician before initiating any new supplement regimen to ensure safety and efficacy.

